-
The Ontario Smart
Home RoadmapThe way we use electricity in our homes is changing. New technologies and services are emerging that will allow home consumers to use electricity in ways that better suit their needs and their budgets. Many smart homes will be able to produce electricity to use within the house, or sell back to the grid.
Click through the roadmap to see how smart homes could evolve in Ontario over the next 20 years.




-
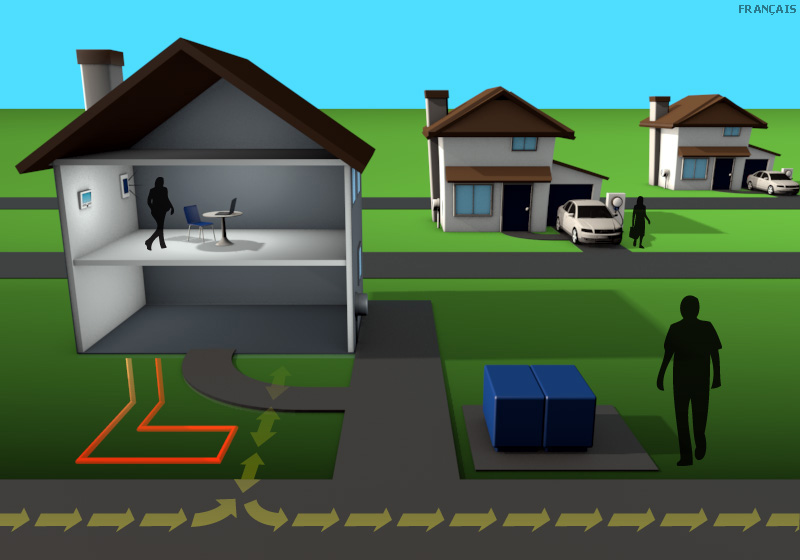
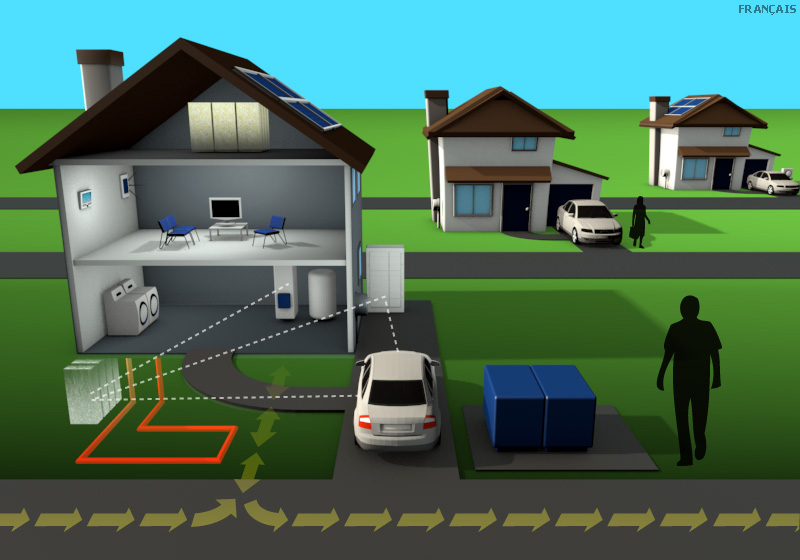
Charging station

A number of electric vehicle pilots are underway, designed to evaluate the impact that vehicle charges have on local distribution systems.
Web portal

Energy use information is readily available to consumers online.
Home gateway device and thermostat

Home automation systems allow consumers to preset indoor home temperatures in response to price and other signals such as the availability of green energy – without sacrificing comfort.
Smart meters

With smart meters tracking hourly energy use, most consumers pay time-of-use rates.
Transformer

Local utilities can more efficiently manage their distribution systems by using new technologies to monitor and control real-time power flows.
Heat pumps

Geothermal systems transfer heat to or from the ground and the home for air conditioning and heating, significantly reducing energy costs and the impact on the environment.
-
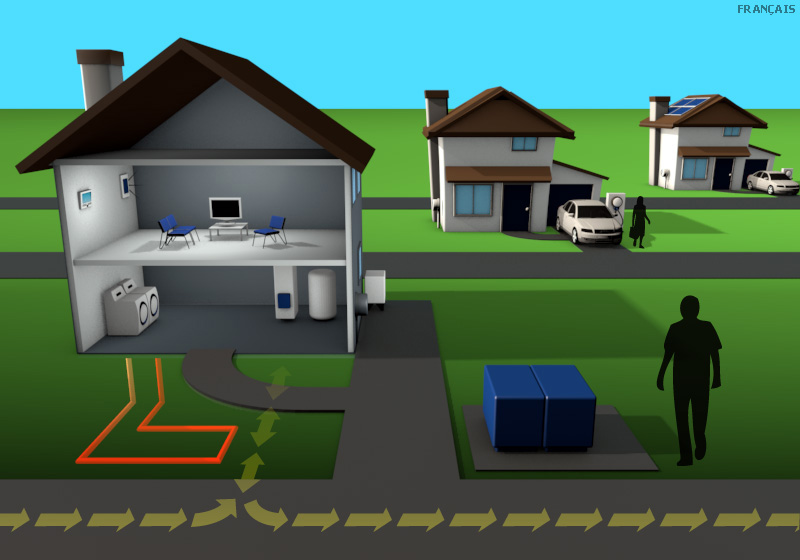
Consumer products and services

More robust consumer offerings are available – such as different time-of-use price plans and demand response programs, many with customized features.
Industry standards

Industry standards are established for most smart home technologies, including electric vehicles.
Solar panel

Growing numbers of Ontarians adopt in-home generation technologies such as solar panels.
Distribution network

Ontario's distribution networks more easily accommodate two-way power flows going into and out of homes as a result of electric cars, storage technologies and in-home generation.
Home gateway device

Home automation systems allow consumers to control their smart appliances and change their energy use in response to price and other signals.
Electricity storage

Used car batteries are recycled and used to store electricity produced during off-peak hours for use during peak hours.
Smart appliances

Smart technologies are embedded in home appliances and interact with home gateway devices. For example, appliances could be programmed by the homeowner to cycle down as part of a demand response program.
-
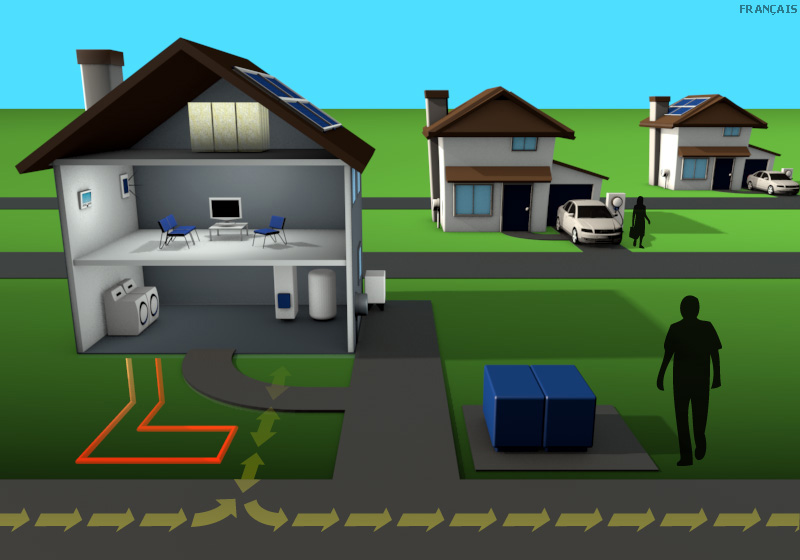
Thermal solar panel

Thermal solar panels continue to become more widely available providing heat for water and other uses, offsetting a home’s electricity use.
Thermal storage

Improvements to thermal energy storage beyond heat pumps allow for the long-term storage of heat energy collected from solar thermal panels.
Home gateway device

Home area networks allow consumers to fully integrate into the operation of the grid. Consumers will be able to sell power to their local utility as well as monitor and control their energy use through mobile and computing devices.
Electric vehicle

The Ontario government envisions that one in 20 cars on the road are powered by electricity.
Photovoltaic solar panel

Photovoltaic panels which produce electricity from the sun continue to become more efficient and are complemented by new energy storage technologies.
-
Fuel switching

Homes can switch between multiple sources of energy.
Small scale
hydrogen storage
Some homeowners choose to install small-scale hydrogen storage tanks which can be used as a car fuel, for heating or to generate electricity through a fuel cell.
Microgrids

Community-level networks known as "microgrids" allow neighbours to share power, isolate themselves from outages and provide energy to the broader power grid.
Electric vehicle

Electric vehicles offer services such as energy storage and power quality support to smart homes and the broader power grid.
Compact fuel cell

Compact fuel cell technologies can convert a variety of fuels - including hydrogen - into both electricity and heat, providing a low-carbon option for home energy needs.
Wireless driveway
charger
A wireless driveway charger consists of a charging plate buried in the ground that charges an electric car through induction, without having to plug it in.
This Roadmap was developed by the Ontario Smart Grid Forum, now known as the Energy Transformation Network of Ontario, in 2011 to provide a timeline for new energy use options for the home consumer. More detail about the roadmap and other aspects of the development of smart grid capabilities in Ontario can be found in the Forum’s 2011 report: Modernizing Ontario’s Electricity System: Next Steps. This roadmap is also available in French.
Best viewed at a screen resolution of 1024x768 or higher | Copyright © 2012 Independent Electricity System Operator